

The whimsically-named loblolly boy was the predecessor to today’s hospital corpsman. For instance, “boy” began in 1798 as a rate for juvenile apprentice Sailors at a time when there was no minimum age for service in the Navy. Each frigate was to have as petty officers two master’s mates, a captain’s clerk, two boatswain’s mates, a coxswain, a sailmaker’s mate, two gunner’s mates, a yeoman of the gun-room, one quarter gunner for every four guns (amounting to eleven for each of the 44-gun, and nine for each of the 36-gun frigates), two carpenter’s mates, an armorer, a steward, a cooper, a master-at-arms, and a cook.Īdditional rates were created early in the Navy’s history.
When the Navy was reestablished in 1794, petty officer complements were specified. As in most administrative matters, the United States Navy followed the Royal Navy’s precedent when it was established.īesides officers and warrant officers, the Continental Congress simply called for enlisted seamen in 1775. Petty officers – a term derived from the French petit, meaning “small” – were appointed by a ship’s captain to fill specific roles onboard ship, and they did not retain their positions when they moved between ships. Common seamen of various grades of skill and experience comprised the vast majority of a ship’s crew and were organized as deemed necessary by the ship’s chain of command. Rates and ratings were one and the same in the eighteenth-century British navy. The history of the Navy’s enlisted rate and rating system, like its counterparts in the officer and warrant officer corps’ rank structure, reflects the Navy’s evolution from a labor-intensive sailing fleet into a technologically-advanced, highly-specialized force with an established system for career advancement in a wide variety of occupational specialties. These Sailors can earn a rating through examination, a process known as “striking for rate.” Those who undertake this process are known as “strikers.” A portion of Sailors enter the fleet “undesignated,” and are assigned to general career paths such as aviation (airman), deck (seaman), and engineering (fireman). Most Sailors achieve their rating through qualification at advanced training schools after basic training. To complicate matters further, the Navy considers Sailors in the E-1 to E-3 pay grades “nonrated,” meaning they do not yet hold a rating. Thus, the Navy combines rates and ratings in Sailors’ titles. A Sailor of equivalent rank/rate with a rating of boatswain’s mate would be Boatswain’s Mate Second Class Jones. For example, where a notional Sergeant Smith may have a military occupational specialty (MOS) of infantryman in the Army, he would simply be designated Sergeant Smith, both in conversation and on official documents. The second unique aspect of Navy enlisted rates is the inextricable linkage of rates, which represent a Sailor’s pay grade, and ratings, which denote an occupational specialty. The first point of divergence is the term “rate,” used in the Navy rather than the more-familiar term “rank,” which is reserved for naval officers and warrant officers. The United States Navy’s enlisted rank and rate system is unique among the armed services.
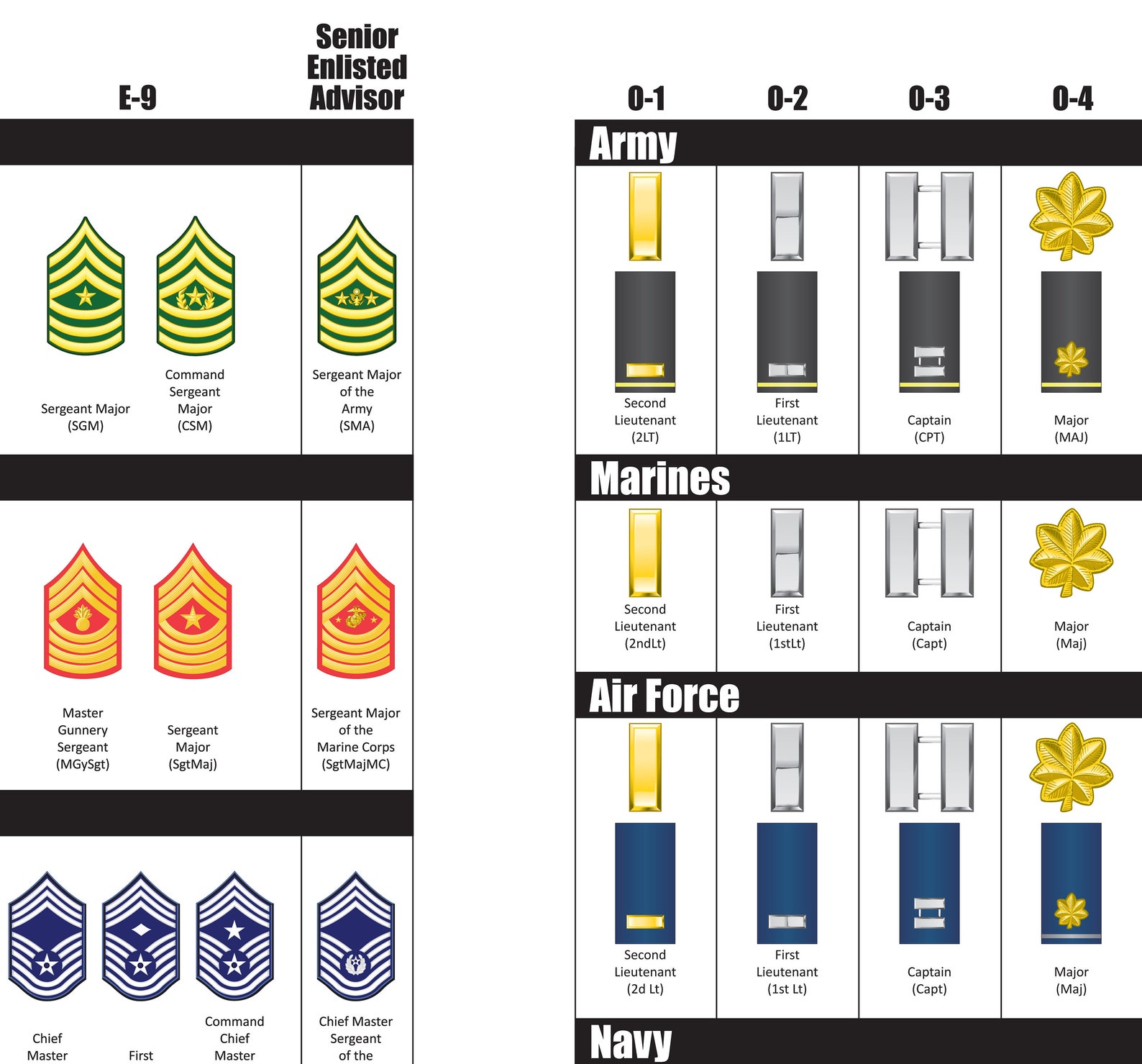
Enlisted ranks series#
The other posts in the series discuss warrant officer ranks () and officer ranks (). The history of Navy ranks is equally complicated, and includes an assortment of ranks that no longer exist and some that have disappeared, reappeared, and disappeared again! In this part of a three-part series, we look at the evolution of the Navy’s commissioned officer ranks. Navy’s unique rank structure can be confusing. To outsiders, especially members of the non-maritime services, the U.S. Moving sergeant to the E-5 grade was meant to restore some of its supervisory status.By Nicholas Roland, Historian, Naval History and Heritage Command With the rank of sergeant at the 4th Grade, the army had more sergeants than lower grades.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
